Resource Library
Start Reading

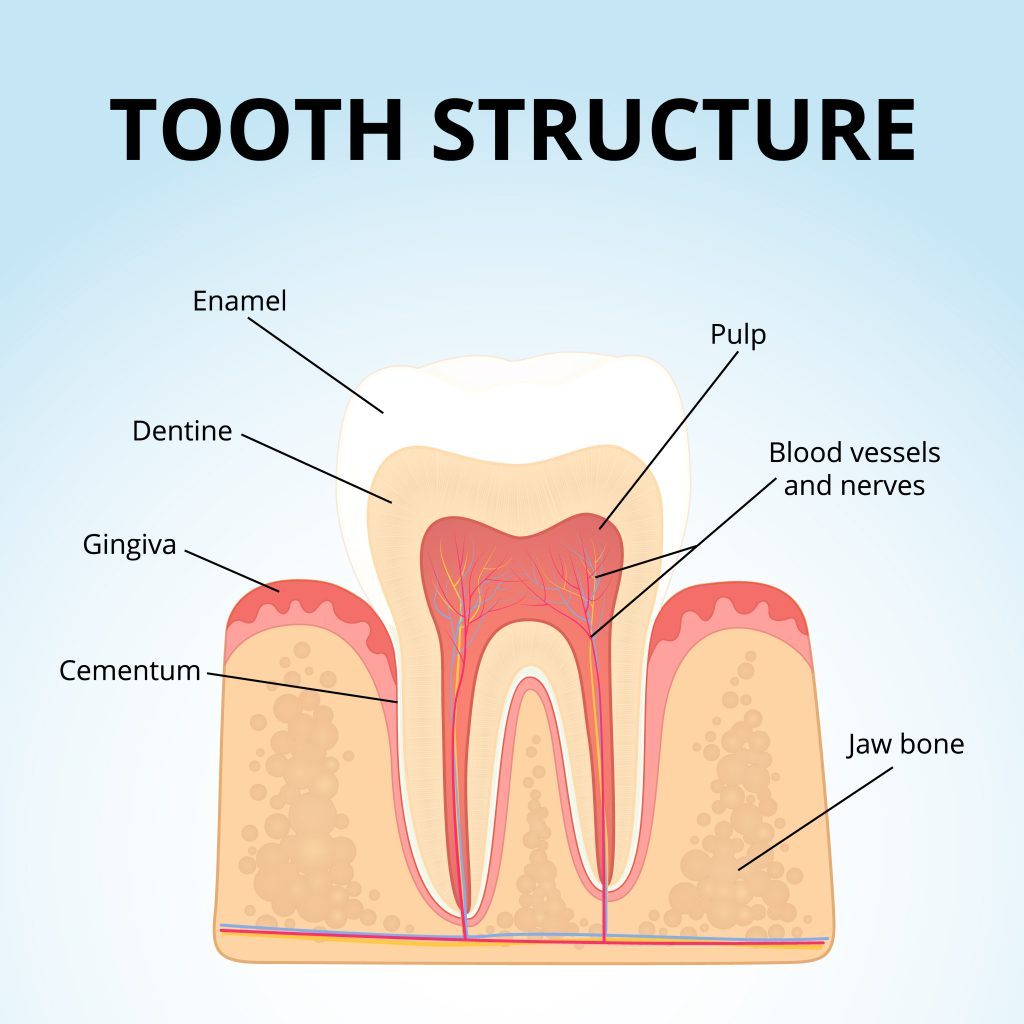
Tooth enamel is a thin outer shell that covers the tooth crown. This protective layer is the hardest tissue in the human body. Tooth enamel protects the teeth from the impact of daily activities such as chewing, crunching, and grinding. Though it’s a tough material, enamel can wear away, chip, or break.
When the enamel becomes weak, your teeth are more vulnerable to dental decay and fracturing, which can eventually result in tooth loss. Can you restore tooth enamel or protect or strengthen it? The answers aren’t exactly simple. Keep reading to learn more—especially about how to prevent erosion in the first place.
Learn about the dramatic difference 55 seconds per day can make for your lifetime oral health with our No-Nonsense Guide to Flossing

Why is tooth enamel important? As a protective outer layer, it protects teeth from decay and bacteria while also strengthening the underlying dentin. It is also responsible for giving teeth their typical white color.
The importance of tooth enamel cannot be overstated, as it protects the nerves and living tissues of the teeth from the acidic attack of plaque. Without a strong outer enamel, you risk developing cavities and experiencing other oral and overall health problems.
 One of the ways that enamel can wear away over time is due to the presence of plaque on the teeth.
One of the ways that enamel can wear away over time is due to the presence of plaque on the teeth.
Plaque is a sticky film comprised of bacteria, food particles, and saliva. It can accumulate between the teeth, around cavity fillings, and along the gum line. Acid is produced when the plaque bacteria feeds on the sugars in the food. That acid gradually eats away at the healthy minerals in the enamel, creating pits on the surface of the teeth.
When a tooth appears yellow, that’s an indicator of enamel erosion. The yellow color is because the yellow layer of dentin beneath becomes exposed. Over time, the pits that develop in the enamel increase in size, which can lead to a tooth infection.
Besides plaque, which can be controlled through regular dental hygiene and reducing sugar intake, there are other causes of tooth erosion:
 The human body’s capacity to restore itself is amazing. Cut nails and hair grow back, and broken bones will self-repair. Does enamel grow back? Unfortunately, the answer is no. Tooth enamel cannot grow back because it is not living tissue. It can’t be naturally regenerated or even artificially regrown.
The human body’s capacity to restore itself is amazing. Cut nails and hair grow back, and broken bones will self-repair. Does enamel grow back? Unfortunately, the answer is no. Tooth enamel cannot grow back because it is not living tissue. It can’t be naturally regenerated or even artificially regrown.
However, some dental products help with tooth enamel restoration, just not in the way you might imagine. They work to remineralize tooth enamel. Your teeth lose minerals daily when bacteria in food and beverages attack your teeth.
Certain kinds of toothpaste and dental products remineralize tooth enamel by pushing calcium and phosphates back into the teeth and hardening the enamel. And fluoride plays a powerful role by capturing the calcium and phosphates that acids draw from the teeth.
Additionally, if you’re suffering from tooth decay or cavities, your dentist can add a sealant that bonds to the enamel. This extra layer of protection isn’t a perfect fix, but it acts as an enamel substitute that can last for many years.
 The best way to prevent tooth enamel erosion is to practice good dental hygiene habits and follow these tips:
The best way to prevent tooth enamel erosion is to practice good dental hygiene habits and follow these tips:
If you’re concerned about the possibility of tooth enamel erosion, then it’s time for a trip to the dentist!
“The Evidence You Need To Pick The Right Dentist” is a chart that can help you choose the right dentist for you and your family. Download it today and learn what separates Penn Dental Family Practice from the rest.
At your visit, your dentist will examine your teeth to determine the extent of the damage and provide recommendations on how to repair tooth enamel and prevent enamel erosion. Besides receiving individualized attention from the dentist, the visit will help to prevent or diagnose cavities that have formed.
Get a head start on tooth erosion before it’s too late. While restoring tooth enamel isn’t possible, strengthening enamel is, and we can help you manage it. To make your appointment at Penn Dental Family Practice, please call our offices at 215-898-PDFP (7337) today!